Research Stories
Filter by category
Filter by year
Filter by year
- Alloys
- Analytical Chemistry
- Anti-Cancer
- Applied Physics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Chemical Biology
- Chemistry
- Clean Energy
- Condensed Matter
- DNA
- Energy
- Environmental Science or Biology
- Food Safety
- Kondo Cloud
- Materials
- Materials Chemistry
- Materials Science
- Mathematical Modelling
- Mathematics
- Nanomaterials
- Neural Networks
- Neutron Scattering
- Photosynthesis
- Photothermal Therapy
- Physics
- Quantum Materials
- Rankings
- Renewable Energy
- RNA
- Soft Matter & Biophysics
- Solar Cell
- Sound Wave
- Spectroscopy and Imaging
- Sustainability
- Theoretical and Computational Physics
- Transition Metal

In the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI), a novel optical “micro-comb” chip developed by a physicist from the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has played a pivotal role in building the fastest optical neural network processor. An international research team has recently demonstrated the world’s fastest and most powerful optical neural network processor, which is capable of operating at faster than 10 trillion operations per second.
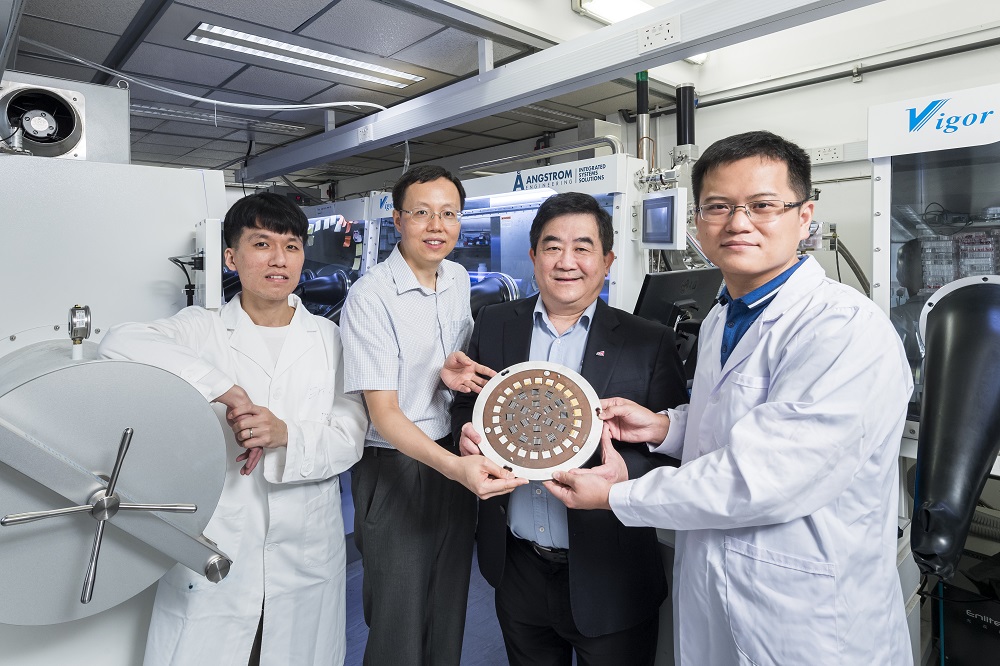

At CityU, Professor Alex Jen Kwan-yue, Lee Shau-Kee Chair Professor of Materials Science, has been working on developing more stable and environmental friendly perovskite and organic solar cells, which are believed to offer more promising and diverse applications to replace silicon as the future of photovoltaic technology.
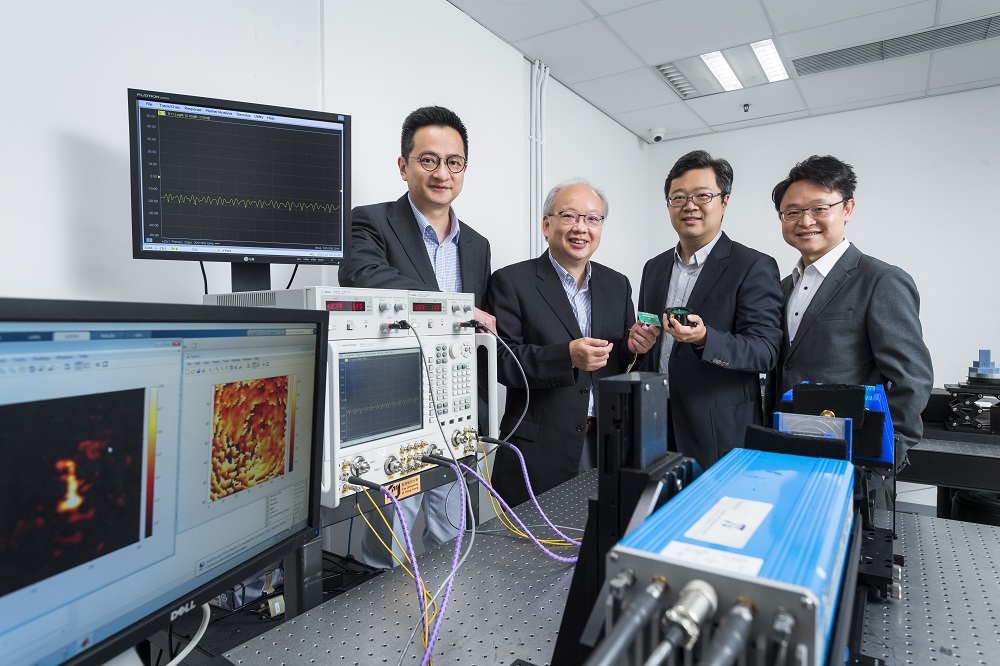
A team of multi-disciplinary experts, led by Professor Chi-hou Chan, Chair Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE) and Director of the State Key Laboratory of Terahertz and Millimeter Waves (SKLTMW) at CityU, has been working on advancing the development of terahertz (THz) technology for 6G communications, imaging and spectroscopy.
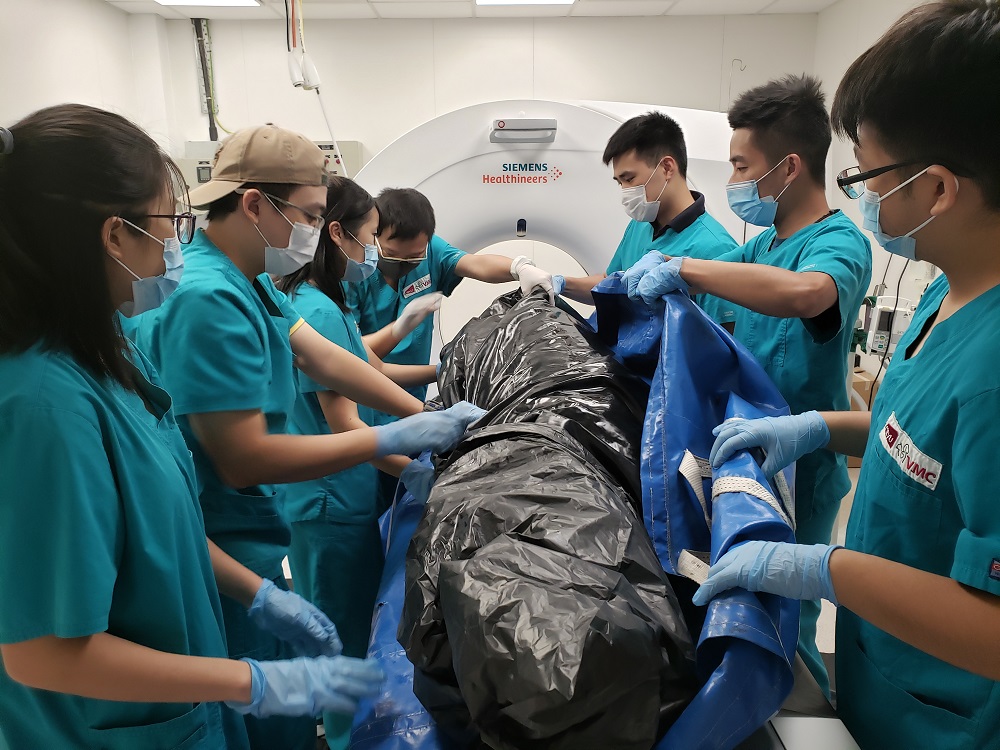
A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) is the first team worldwide to routinely apply “virtopsy”, a pioneer dead body examination technique, on stranded cetaceans to find out their causes of death, health conditions, as well as the anthropogenic impact on their well-being.
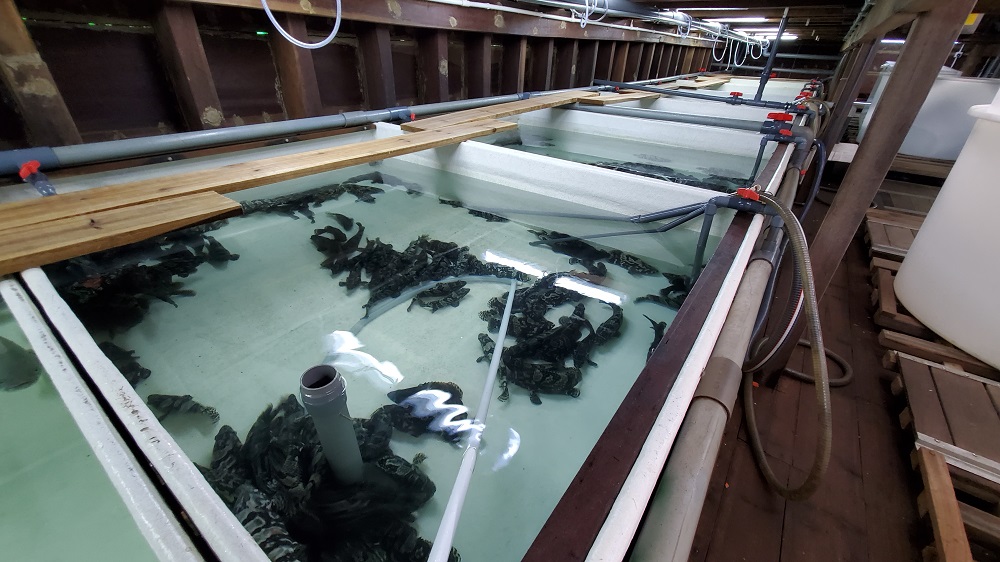

To protect the marine ecological environment and facilitate the sustainable development of the marine economy in Hong Kong, a CityU-led marine research team has developed a new aquaculture technique by establishing a floating, indoor weatherproof fish farm with a seawater recirculating system to replace conventional fish rafts.

A joint research team co-led by a scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed a much more stable, manganese-based cathode material. The new material has higher capacity and is more durable than the existing cobalt and nickel cathode materials - 90% of capacity is retained even when the number of charging-recharging cycles doubled.