Research Stories
Filter by category
Filter by year
Filter by year
- Alloys
- Analytical Chemistry
- Anti-Cancer
- Chemical Biology
- Chemistry
- Clean Energy
- Energy
- Environmental Science or Biology
- Food Safety
- Materials
- Materials Chemistry
- Materials Science
- Mathematics
- Nanomaterials
- Photosynthesis
- Physics
- Rankings
- Renewable Energy
- RNA
- Solar Cell
- Spectroscopy and Imaging
- Sustainability
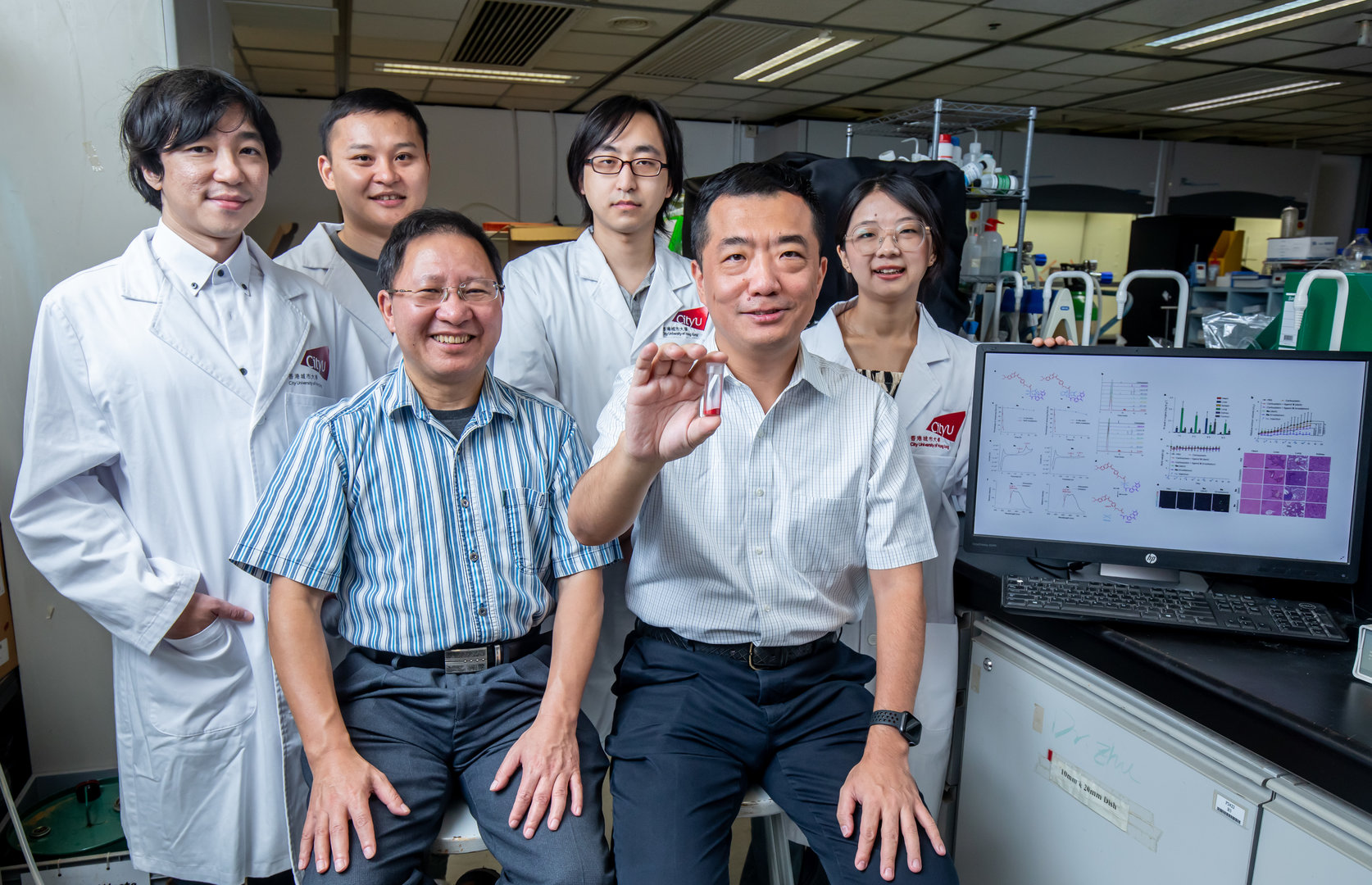

A research team led by scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has achieved a significant breakthrough by inventing a new class of near-infrared-activated photo-oxidants that can effectively kill cancer cells without requiring oxygen.

An international team led by CityU has announced a groundbreaking step forward by successfully developing a highly efficient electrocatalyst that can enhance hydrogen generation through electrocatalytic water splitting. The discovery was published in one of the world’s premier science journals, Nature.
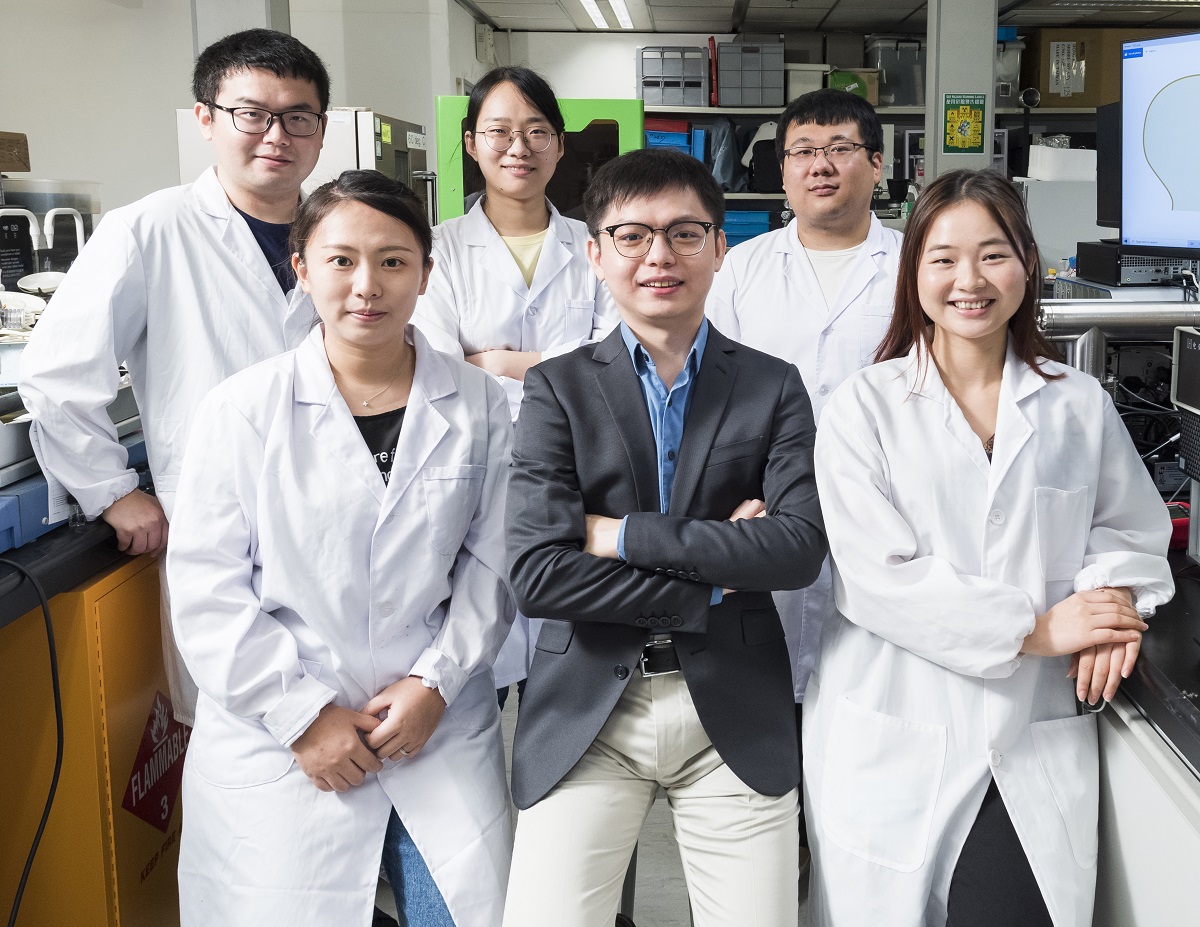

A joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and collaborators recently developed a stable artificial photocatalytic system that is more efficient than natural photosynthesis.

With the support of the State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution, a cross-institutional study involving the Education University of Hong Kong, the City University of Hong Kong, and the University of Hong Kong, has uncovered a promising new method for monitoring radionuclides in the ocean.
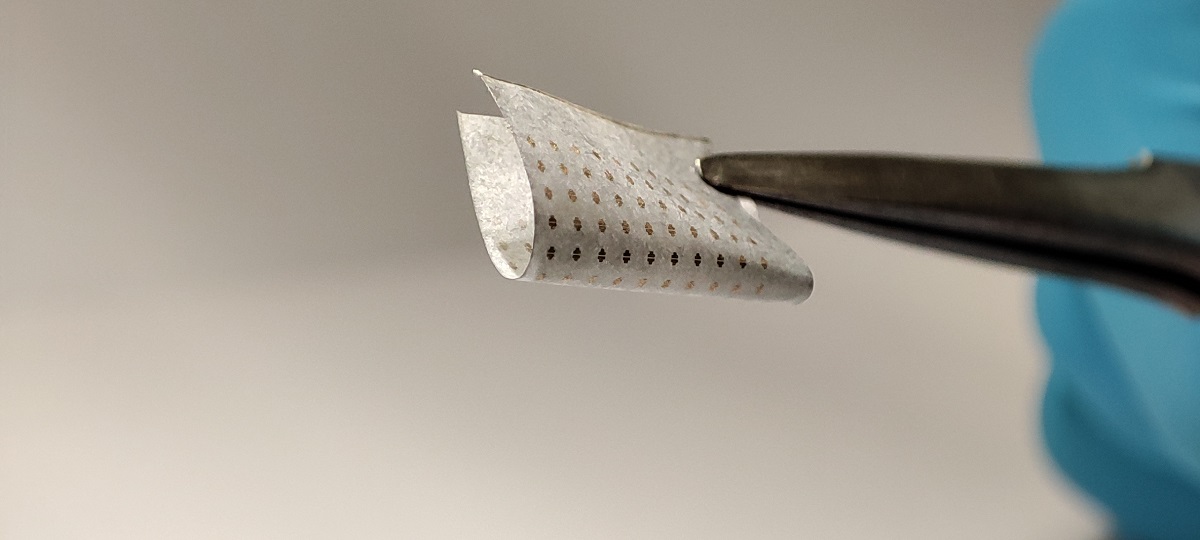
A collaborative team led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented an innovative method for synthesizing high-quality, semiconducting nanomesh at a lower temperature and production cost than conventional methods. The findings will help enable the large-scale production of nanomesh for next-generation electronics.
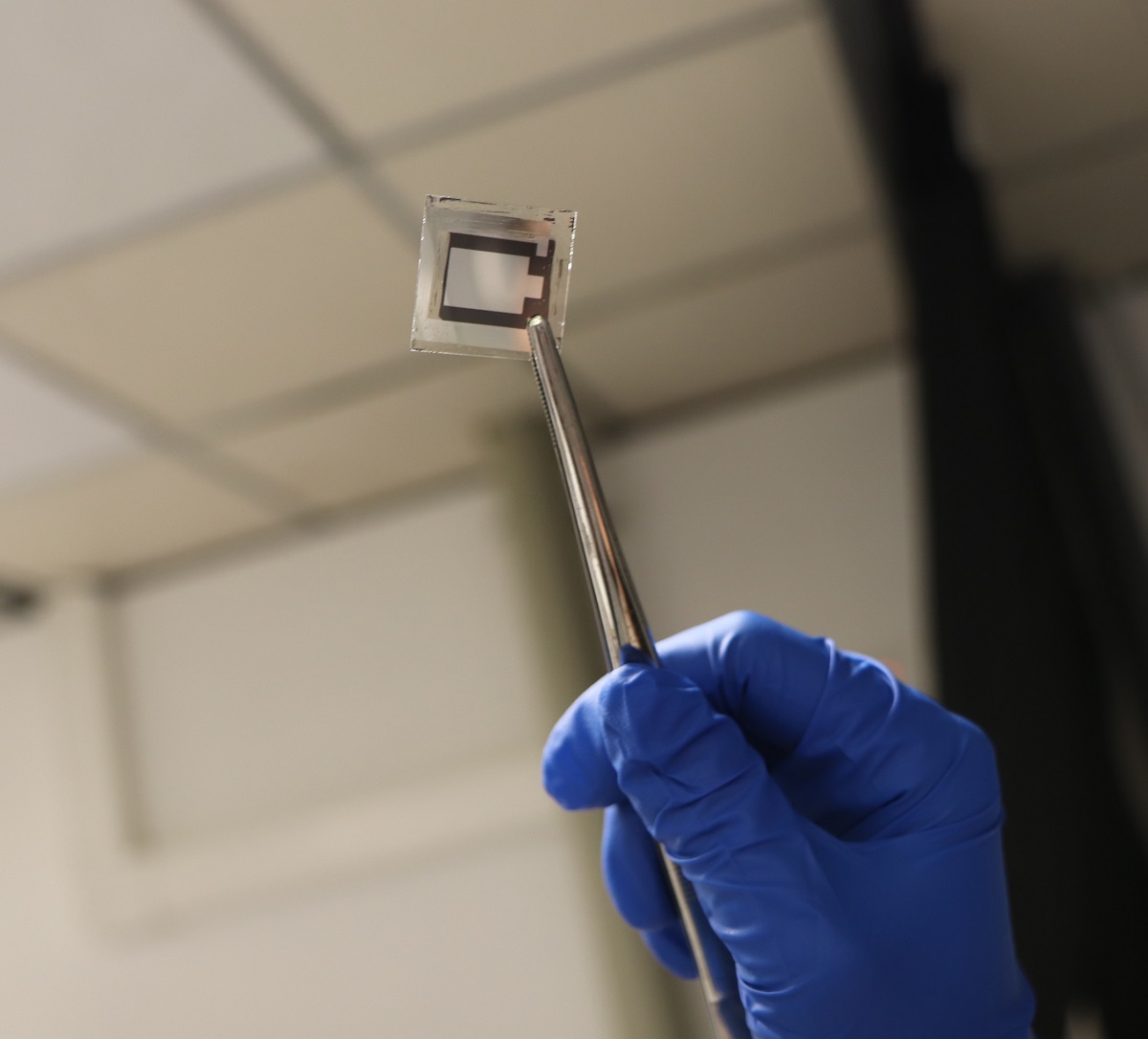

Perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) are a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based solar cells because of their high power-conversion efficiency and low cost. However, one of the major challenges in their development has been achieving long-term stability.