Research Stories
Filter by category
Filter by year
Filter by year
- Alloys
- Analytical Chemistry
- Anti-Cancer
- Applied Physics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Chemical Biology
- Chemistry
- Clean Energy
- Condensed Matter
- DNA
- Energy
- Environmental Science or Biology
- Food Safety
- Kondo Cloud
- Materials
- Materials Chemistry
- Materials Science
- Mathematical Modelling
- Mathematics
- Nanomaterials
- Neural Networks
- Neutron Scattering
- Photosynthesis
- Photothermal Therapy
- Physics
- Quantum Materials
- Rankings
- Renewable Energy
- RNA
- Soft Matter & Biophysics
- Solar Cell
- Sound Wave
- Spectroscopy and Imaging
- Sustainability
- Theoretical and Computational Physics
- Transition Metal

City University of Hong Kong (CityU) encourages research and innovation. By translating new knowledge and discoveries into applications, CityU contributes to the development of society.

The State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has been endorsed by the United Nations (UN) to initiate a ten-year "Global Estuaries Monitoring (GEM)" Programme (www.globalestuaries.org) to collect and study environmental pollutants in the estuaries of major cities around the globe so as to formulate a long-term policy of promoting clean estuaries.

Innovative synthesis technique to unveil the crystal structures of next-generation TMD nanomaterials
A collaborative research team led by scientists from the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently overcame the barrier by developing a novel synthesis technique that combines the advantages of closed-system preparation of precursors and gas-solid reaction to produce a number of high-quality and pure unconventional metastable TMD materials in large quantities.

Glass is one of the most common subjects we see every day, but the detailed structure of this non-metallic and non-liquid material has always been a major mystery in science. A research team co-led by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has successfully discovered that the amorphous and crystalline metallic glass have the same structural building blocks.
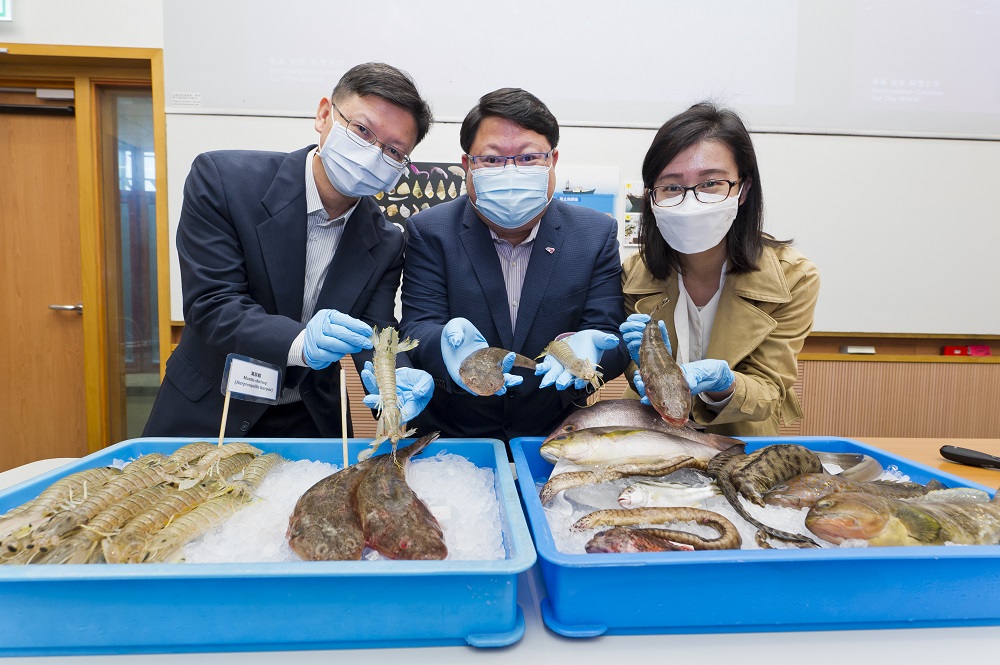

Biodiversity is of crucial importance to the marine ecosystem. The prohibition of trawling activities in the Hong Kong marine environment for two and a half years has significantly improved biodiversity, an inter-university study led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has found.
At CityU, an expert in neutron-scattering measurements has applied this state-of-the-art experimental technique to find out the deformation and transformation behaviours in complex materials, in particular at ultra-low temperatures, opening up a new area of materials research.