Web 2.0: The Next Step in the Evolution of the Web
The way that the Web is being used nowadays has changed tremendously over the years. Instead of merely browsing the Internet, people are now participating and jointly creating and publishing content. In other words, while initially content was mostly "read" from the Web, content is now more and more "written" to the Web through blogs, wikis, communities, tagging and so on. This is why some people refer Web 2.0 as "read/write Web". A new wave of jargons, brands and Web experiences has thus emerged: MySpace, Google Maps, Gmail, FaceBook, Wikipedia, Flickr.com, del.icio.us (social bookmarking), Twitter, YouTube, Mashups, Blogs, and RSS Newsfeeds, just to name a few.
So what does Web 2.0 really mean and what impact does it have on us? The term Web 2.0 is not easily definable. In fact, there had been quite a few open discussions and dispute regarding its definition. Some say Web 2.0 is a perceived second generation of web-based communities and hosted services. Others refer it as a platform i.e. a shared infrastructure and standards such as RSS, XML, AJAX, API's, structured microcontent, read/write web tools like blogging and podcasting, web services, etc., on top of which people can build communities, collaboration, communication and commerce. However, others argue that the term means something different. As the Birmingham Post put it in December 2005, "Typically, a Web 2.0 service is one that uses the very latest technologies to provide a website that works more like an application on your desktop." And others suggest it can include the idea of taking various sources of Web information and mixing them to make a new interactive service, for which the term mash-up (e.g. http://www.netvibes.com/) has been originated in the music industry. Perhaps a good way of explaining what Web 2.0 means is to illustrate this concept in the form of a diagram made by aYsoon Blog.
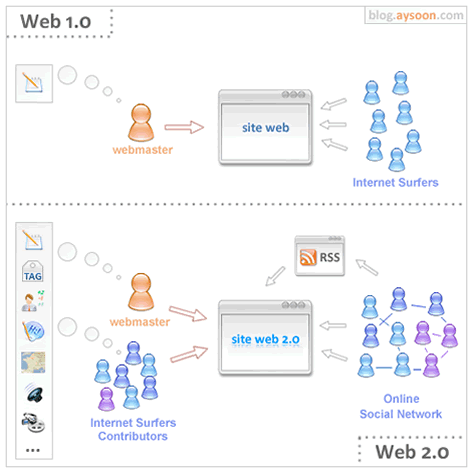
As compared with Web 1.0 which was mostly comprised of static HTML pages, Web 2.0 has much richer "content" shared over the Web, establishing a much stronger user participation and interaction (often referred to as "Collection Intelligence") that includes RSS Feeds and the use of social networking sites. Probably the most popular among the latter is MySpace, a Web site that let people create profiles about themselves, embed music, share videos with other friends and post photos, messages and updates about their daily lives. Other social networking sites include Facebook, geared to college students, LinkedIn, aimed at professionals, and Xanga, a blog-based community site.
Below is a reduced version of a table demonstrating advancements from 1.0 to 2.0 (O'Reilly, 2006)
|
Web 1.0 |
Web 2.0 |
|
|
DoubleClick |
→ |
Google AdSense |
|
Ofoto |
→ |
Flickr |
|
Content management |
→ |
wikis |
|
systems |
|
|
|
Britannica Online |
→ |
Wikipedia |
|
Personal websites |
→ |
Blogging (Myspace) |
|
Taxonomy |
→ |
Tagging |
|
Publishing |
→ |
Participation (youtube) |
Needless to say, Web 2.0 is all about openness and sharing and the demand for "user-generated content" has never been greater. Successful examples that demonstrate the Web 2.0 concepts are:
- Google: Probably the most successful company utilizing Web 2.0 concepts. Google learns from user's links to web sites, as well as user search behavior, and uses that to deliver better search results. That's typically Web 2.0, even though the users are not conscious that they are "contributing" to Google. In addition, numerous Google services are accessible via Web services.
- Amazon: A mega-large online bookseller. Amazon revolutionized book selling in the sense that it had a strong connection to and involvement with its user base or customers by enabling them to write reviews on its books and other products. It also lists related buyer recommendations with each of its online merchandise. "Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought," is the label familiar to many readers. In addition, Amazon has developed their database of book information to the point where other sites utilize it. Its data is accessible via public Web services.
- eBay: No site provides a better demonstration of user involvement than eBay. It grows organically with user (buyers and sellers) activity, and the various features of eBay are available via public Web services.
- Wikipedia: This site is the ultimate example of online collaboration. With more than one million entries, Wikipedia is the largest encyclopedia on the Internet. It is a mega-wiki site that allows anyone on the Internet to edit the content published on it. It relies on a great deal of trust but the idea is that with so many people providing input on the topics, the data will remain correct and up to date.
- Blogging: Another great example of collaboration and placing content creation in the hands of the user. Basically a blog is an online personal record that is being updated on an ad hoc or a regular basis with new entries appearing at the top of the list and old entries can be viewed from an archive. In other words, anyone with an Internet connection will be able to start their own global publication. RSS has increased the demand of blogs because they allow users to subscribe to other people’s blogs so that they can be notified when new entries are added. Nokia has produced software called "Live Blog" which enables users to publish blog entries whilst on the move using a mobile phone; it can also make use of the phone cameras to add videos and images to their blogs.
- An example of a technology or approach to come out of the Web 2.0 is AJAX, a scripting technique that enables page content to be updated without the need for the entire page to be loaded. It can be very powerful when combined with technologies such as RSS to produce live content on a website. Its main functionality stems from an exploitation of XMLHttpRequest, a JavaScript class (with specific properties and methods) supported by Internet Explorer, Firefox, and other modern browsers. The fact that the browsers that support it have become more common makes AJAX a popular way of developing powerful Web applications over the years. A well known example is Google’s Gmail mail client which uses AJAX to make a fast-responding email application i.e. you can delete messages and perform other tasks without waiting for a new page to load. Google Earth and Google Maps are other examples of successful AJAX implementation.
The above listed sample applications and technology are just a sampling of what is currently available, but it does provide an idea of what is expected from the next generation of websites.
Conclusion
Web 2.0 is not an individual technology but instead is a set of principles that represents the next step in the evolution of the World Wide Web. Whether it is referred to as "Web 2.0"or not, Web applications and services will continue to develop in the age of rapid technological advance we are currently in and become more and more user orientated. Despite its popularity and usefulness, like all new technologies, Web 2.0 has added another dimension of security risks. We will cover the other side of the story in the coming issue. Stay tuned!
References
- What is Web 2.0? (Tim O'Reilly)
http://www.oreillynet.com/pub/a/oreilly/tim/news/2005/09/30/what-is-web-20.html
- Web 2.0 Resources on TechRepublic
http://search.techrepublic.com.com/search/Web+2.0.html
- Unleashing Web 2.0 : from concepts to creativity (Gottfried Vossen)
- PC Pro: Features – Web 2.0
http://www.pcpro.co.uk/features/100742/web-20.html?searchString=web+2+0