Migrating to Cloud
by JUCC ISTF
/* The following article is extracted from the "Information Security Newsletter" published by the JUCC IS Task Force. */
|
?The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing1
The cloud model is composed of 5 essential characteristics (Ondemand self-services; Broad network access; Resource pooling; Rapid elasticity and Measured service), 3 service models (Software as a Service; Platform as a Service and Infrastructure as a Service) and 4 deployment models (Private cloud; Community cloud; Public cloud and Hybrid cloud).
|
Cloud computing has provided an alternative means of utilizing computing resources. In the past, Universities, whether large or small, have to perform the following in order to acquire computing power for processing: procure its own hardware and software, setup the infrastructure and applications, manage and maintain the hardware and software assets, and eventually dispose or upgrade when the IT systems become end of life. With cloud computing, the same university now has the option of utilizing computer resources offered by the cloud service provider instead of procuring and managing its own resources.
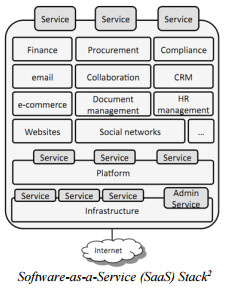
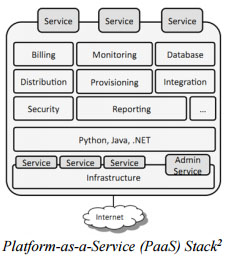
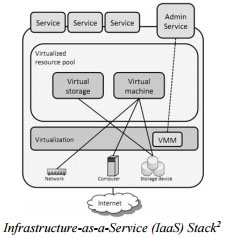
Cloud Models Consideration
Universities thinking of using public cloud service can choose one of the three cloud service delivery models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The terms of services and contractual agreements of these delivery models can be very different. Universities need to study the relevant terms of services to understand the agreements such as licensing rights, usage restrictions, service level agreements, data protection and ownership arrangements, liabilities, termination arrangements, etc.
There are many benefits of adopting cloud computing including attractive financial model of paid, broader network access coverage covering heterogeneous platform of end point devices, availability of services independent of location and time of access, and easing the management of IT resources. Despite these benefits, IT security is one of the key concerns which should not be overlooked.
This newsletter will describe what Universities should consider in order to address various IT security issues when thinking of migrating their internal IT services to the public cloud. This article assumes that the audience has basic understanding of cloud computing, and will only focus on describing the IT security considerations.



Cloud Models Consideration
Universities thinking of using public cloud service can choose one of the three cloud service delivery models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The terms of services and contractual agreements of these delivery models can be very different. Universities need to study the relevant terms of services to understand the agreements such as licensing rights, usage restrictions, service level agreements, data protection and ownership arrangements, liabilities, termination arrangements, etc.
Not only should Universities understand type of risks associated with the choice of a cloud service provider, Universities should also ask cloud service providers to explain what security features they have built in and made available, past records of encountering and handling of IT security and service outage incidents, service level management and performance monitoring.
|
Cloud Migrations: Don't Forget About The Data3
Focus on your data migration separately from your application migration to get better results.
Data migration consists of three parts: the migration lifecycle on your data subsystem, the transfer of legacy data, and, finally, the integration with the rest of the migrated application. Let's examine each in more detail:
1. Data Migration Lifecycle |
Data Migration Planning