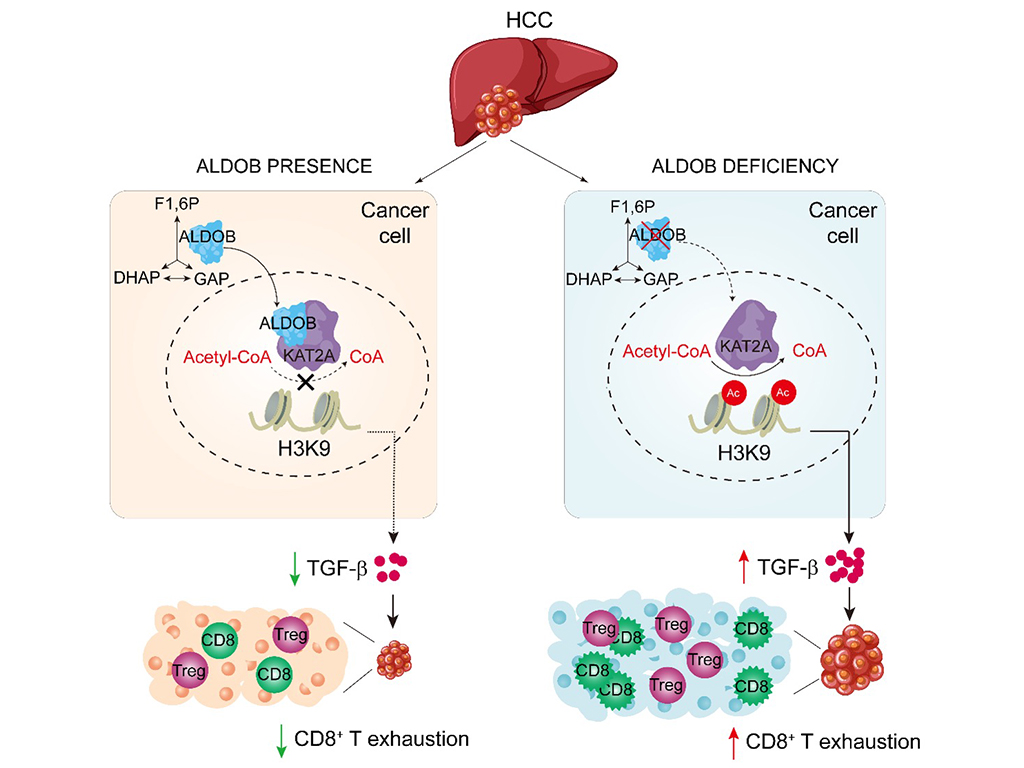
Immunotherapy has revolutionised cancer treatment, but the clinical responses in liver cancer remains are far from satisfactory. To address this, scientists have been investigating the metabolic interactions between immune cells and tumour cells in the tumour microenvironment (TME). Previous studies led by Prof. Yin and other researchers have identified that downregulation of a glycolytic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase B (ALDOB) in tumour cells orchestrated metabolic programming to favour hepatocellular carcinogenesis (HCC) (Li et al, Nature Cancer, 2020; He et al, Plos Biology, 2020; Liu et al, Hepatology, 2021). However, it was elusive how ALDOB expression in tumour cells affects the TME in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
In a recent publication in Hepatology, Prof. Yin’s team published a paper entitled “ALDOB/KAT2A Interactions Epigenetically Modulating TGF-β Expression and T Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis”. The research showed that ALDOB downregulation was negatively correlated with CD8+ T cell infiltration in human HCC tumour tissues but in a state of exhaustion. Similar observations were made in mice with liver-specific ALDOB knockout or in subcutaneous tumour models with ALDOB knockdown. Moreover, ALDOB deficiency in tumour cells upregulates TGF-β expression, thereby increasing the number of Treg cells and impairing the activity of CD8+ T cells. Consistently, a combination of low ALDOB and high TGF-β expression exhibited the worst overall survival for HCC patients. More importantly, the simultaneous blocking of TGF-β and PD-1 with antibodies additively inhibited tumorigenesis induced by ALDOB deficiency in mice. Further mechanistic experiments demonstrated that ALDOB enters the nucleus and interacts with lysine acetyltransferase 2A (KAT2A), leading to inhibition of H3K9 acetylation and thereby suppressing TGFB1 transcription. Consistently, inhibition of KAT2A activity by small molecule inhibitors suppressed TGF-β and HCC.
These findings unveil a novel mechanism by which a metabolic enzyme in tumour cells epigenetically modulates TGF-β signalling, enabling cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and influence the response to immunotherapy.
Dr Chunzhao Yin, a Research Assistant at BMS of City University Hong Kong, and Dr Cunzhen Zhang from Shanghai Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital are the co-first authors of the paper. Dr Yongzhen Tao from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH), Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Dr Nan Li from Shanghai Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital are the co-corresponding authors. The research received support from the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, Shenzhen Medical Academy of Research and Translation (SMART), and a startup fund from City University of Hong Kong.