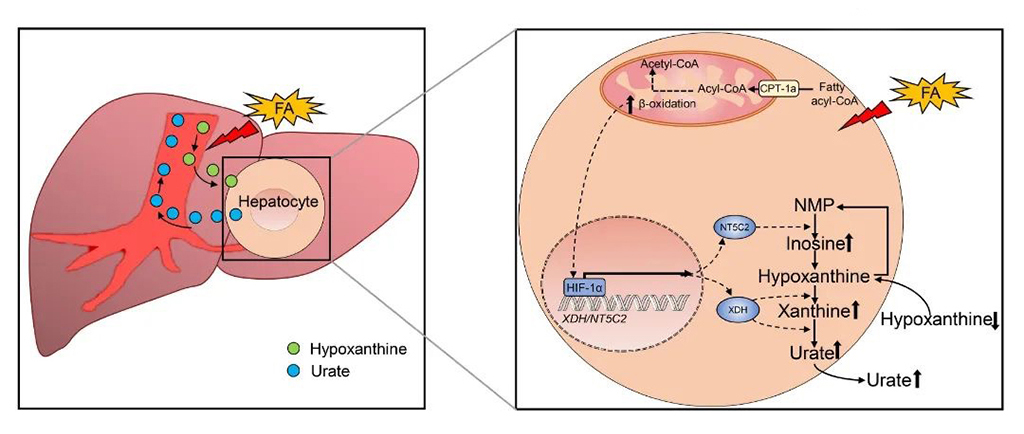
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is diagnosed when the levels of urate in the blood exceed 420 µM, the saturated concentration of urate. In mainland China, the prevalence of hyperuricemia exceeds 17.7% in the adult population, affecting over 185 million individuals. HUA has become the fourth most common chronic metabolic condition in China, following hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, and hypertension. Hyperuricemia not only triggers gout but also increases the risk of various metabolic diseases, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, hypertension, and kidney disease. Among the 25 million gout patients in China, more than half exhibit abnormal blood lipid levels. Although preliminary analysis suggests that hypertriglyceridemia may be a causal factor for HUA, the underlying mechanism has remained elusive.
Recently, Professor YIN Huiyong’s team unveiled a mechanism by which the fatty acid oxidation induces hepatic urate synthesis and HUA. Their findings were published online in Life Metabolism entitled “Fatty acid oxidation-induced HIF-1α activation facilitates hepatic urate synthesis through upregulating NT5C2 and XDH”. They reported that in metabolic disorders, such as hypertriglyceridemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic fatty acid oxidation induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), which transcriptionally activates the urate synthesis pathway involving xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) and cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase II (NT5C2) (Figure above). This mechanism represents the first discovery of a bridging role between lipid metabolism and purine metabolism pathways in metabolic diseases, offering potential strategies for the prevention and treatment of hyperlipidemia and HUA.
This study was carried out through collaborations between the research team led by Professor YIN Huiyong from City University of Hong Kong, the team of Professor XIA Qiang from Renji Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, and the team led by Professor LI Changgui at Qingdao University Affiliated Hospital. Dr Liang Ningning, a Research Assistant in the Department of Biomedical Sciences at City University of Hong Kong, and Dr Yuan Xuan from the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University are the co-first authors, while Professors YIN, Professor XIA, and Professor LI are the co-corresponding authors. This research was financially supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, City University of Hong Kong, and the Shenzhen Institute of Medicine and Research Fund (SMARF). This research was also supported by Professor Robert Terkeltaub of the University of California, San Diego Professor Nicola Dalbeth at the University of Auckland in New Zealand, and Professor Tony Merriman at the University of Alabama at Birmingham in the United States.