Research Stories
Filter by category
Filter by year
Filter by year
- Alloys
- Analytical Chemistry
- Anti-Cancer
- Applied Physics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Chemical Biology
- Chemistry
- Clean Energy
- Condensed Matter
- DNA
- Energy
- Environmental Science or Biology
- Food Safety
- Kondo Cloud
- Materials
- Materials Chemistry
- Materials Science
- Mathematical Modelling
- Mathematics
- Nanomaterials
- Neural Networks
- Neutron Scattering
- Photosynthesis
- Photothermal Therapy
- Physics
- Quantum Materials
- Rankings
- Renewable Energy
- RNA
- Soft Matter & Biophysics
- Solar Cell
- Sound Wave
- Spectroscopy and Imaging
- Sustainability
- Theoretical and Computational Physics
- Transition Metal
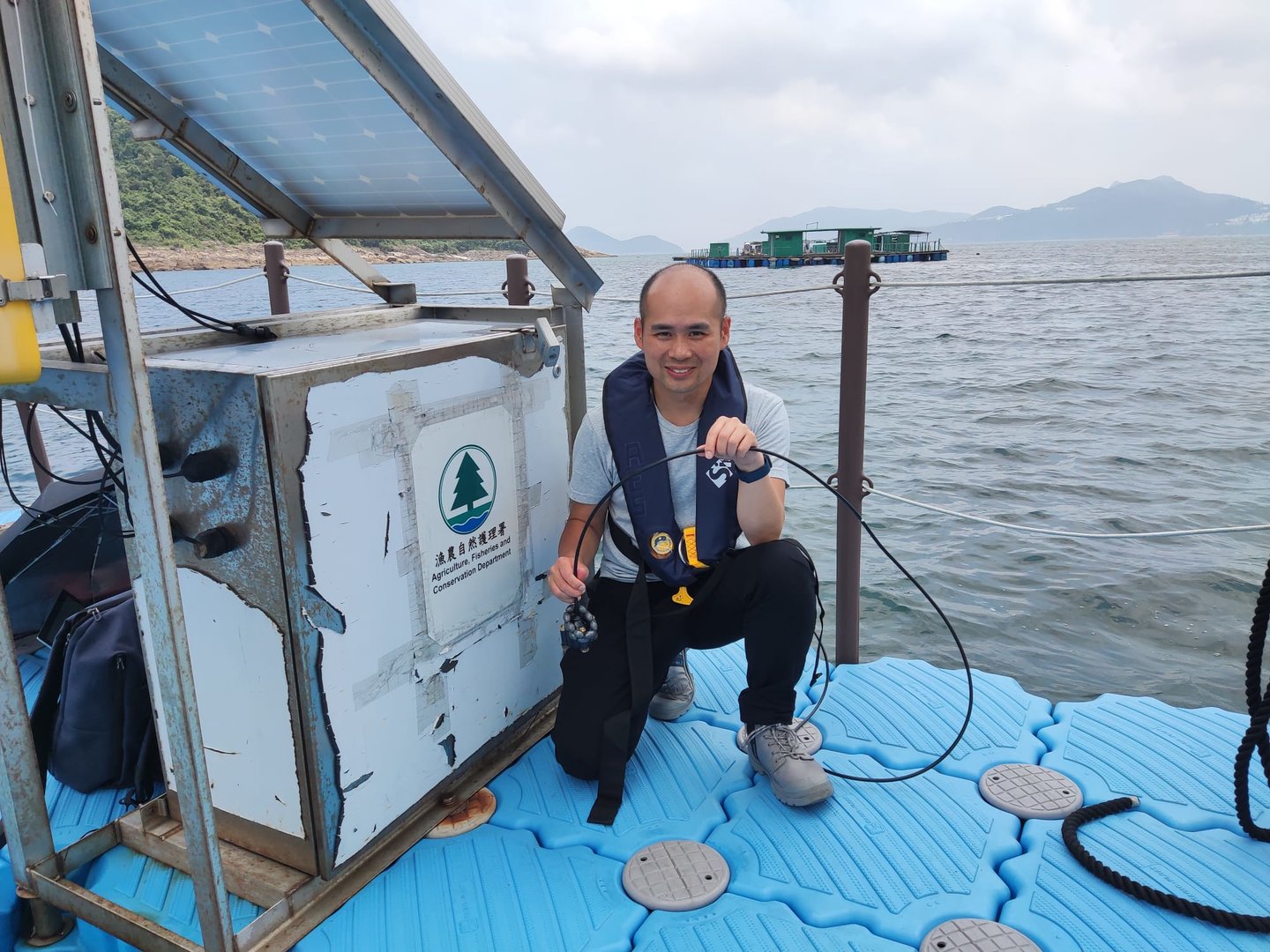

A few years ago, Dr. Chi-on Ng, a graduate of the Department of Chemistry at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK), together with his team, developed a new type of photo-sensor that can effectively monitor oxygen concentration in seawater and reduce the monitoring cost. The team subsequently established a start-up company called “NerOcean”.

Zinc-nitrate batteries are a primary non-rechargeable energy storage system that utilizes the redox potential difference between zinc and nitrate ions to store and release electrical energy. A research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) have developed a high-performance rechargeable zinc-nitrate/ethanol battery by introducing an innovative catalyst. They successfully designed and synthesized an efficient tetraphenylporphyrin (tpp) modified heterophase rhodium-copper alloy metallene (RhCu M-tpp). This bifunctional catalyst exhibits remarkable capabilities in both the electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction (NO3RR) and ethanol oxidation reaction (EOR) in a neutral medium, overcoming the monofunctional limitations of traditional metal-based solid catalysts and providing a valuable reference for the design of sustainable energy storage in the future.

G-quadruplexes (G4), which are special structures in DNA and RNA that play a crucial role in cells, have been associated with cancers and neurological diseases. A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) recently built a new platform to select L-RNA aptamers that can target functional G4 structures. They found an L-RNA aptamer called L-Apt12-6 that binds specifically to a specific topology of G4 structure: parallel G4. The findings may be beneficial for developing new drugs and treatments for G4-related diseases, like cancers.

Electrocatalysis plays a vital role in developing clean energy, greenhouse gas removal and energy storage technologies. A study co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) researchers found that single-walled carbon nanotubes are excellent substrates for enhancing greenhouse gas conversion through molecular curvature. By using these nanotubes as support to induce strain on an electrocatalyst, the efficiency of carbon dioxide reduction to methanol can be significantly improved. This breakthrough opens avenues for developing curved molecular electrocatalysts to efficiently convert carbon dioxide (CO2), one of the key greenhouse gases, into useful chemicals and fuels, thus reducing carbon emission .
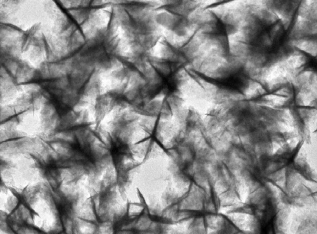
A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently engineered a bimetallic alloy as an ultrathin nanocatalyst that can deliver greatly improved electrochemical performance for generating ammonia from nitrate, offering great potential for obtaining carbon-neutral fuel in the future.
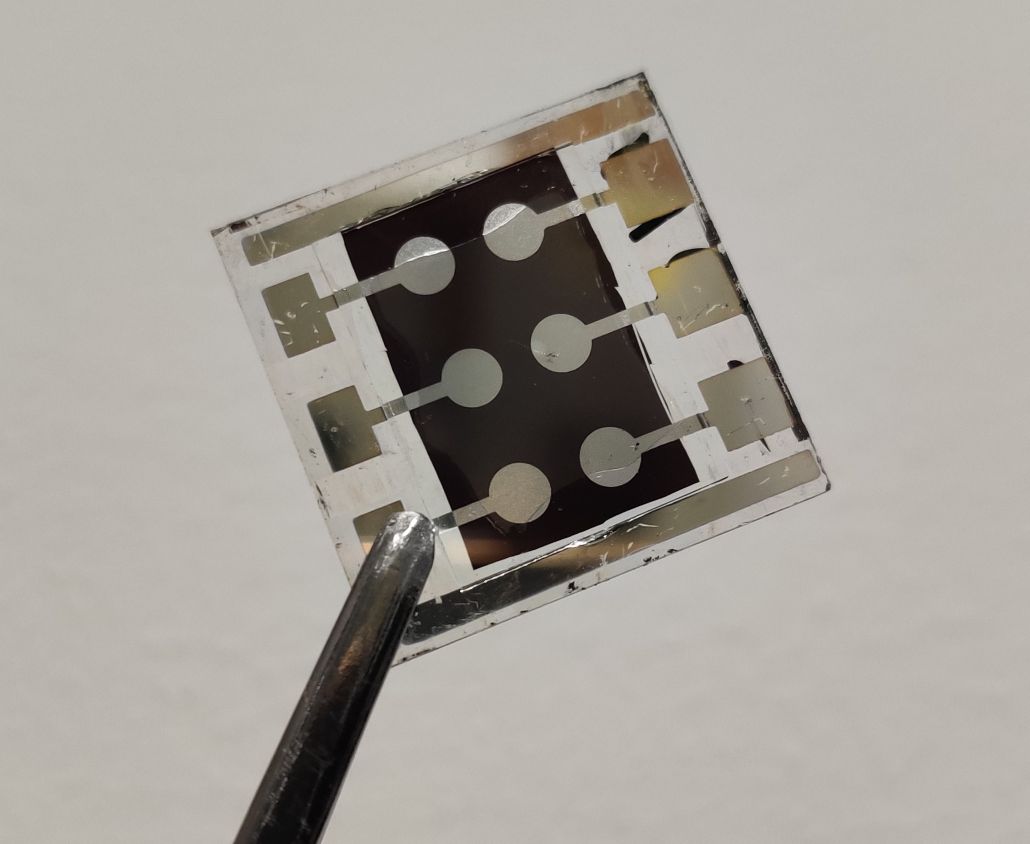
A huge step forward in the evolution of perovskite solar cells recorded by researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) will have significant implications for renewable energy development.