Opportunity
Only around 20% of electronic waste (e-waste) originating from mobile computing devices is currently recycled. Given the predicted annual e-waste generation rate of ~75 million tons by 2030, a huge volume of metals is being inappropriately discarded in landfills. Landfilled metals can leak into the environment, degrading water and soil quality and thus threatening human health and agriculture. Therefore, recycling metals from e-waste, e.g. waste printed circuit boards, is of economic and ecological importance, with the potential to regenerate valuable metals and save energy. Slurry electrolysis (SE) is a promising method of leaching metals from e-waste. However, the requirement of a highly acidic electrolyte necessitates the use of precious metals in the anode, which reduces economic viability. Potential solvent alternatives to strong acids may themselves be expensive or toxic. Hence, there is a need for an improved SE-based method of metal recovery from e-waste that is safe and economical.
Technology
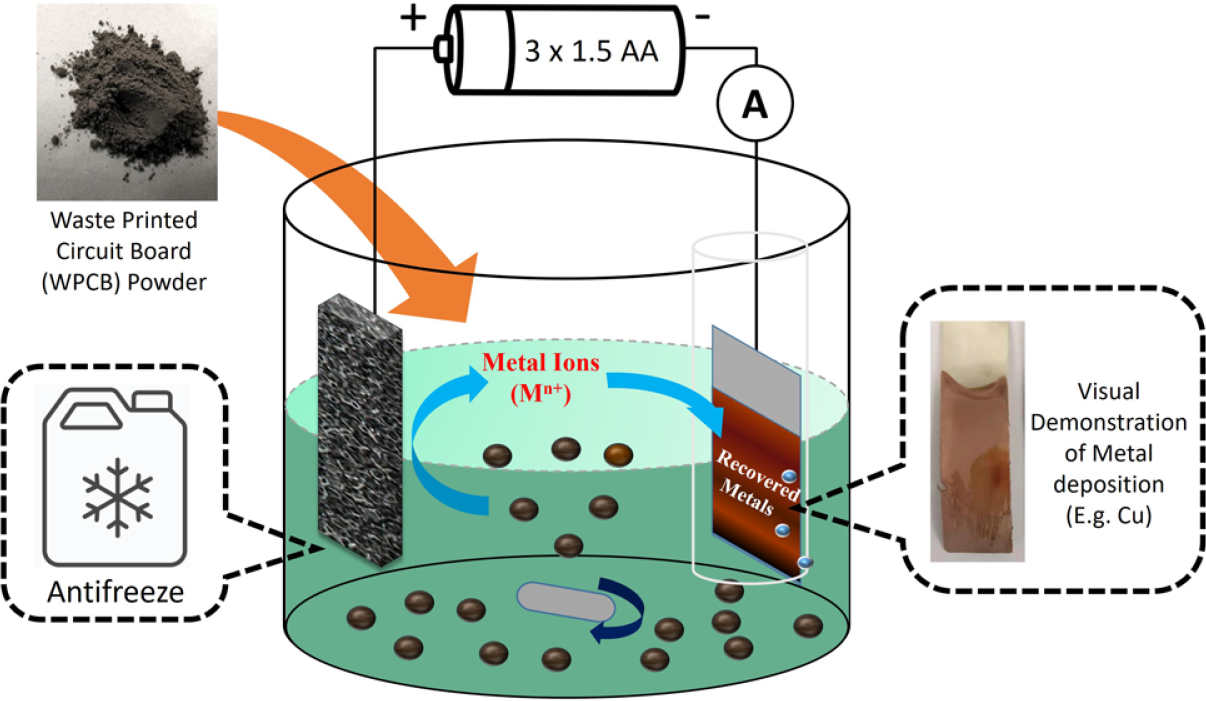
The invention comprises a method of recovering metals from waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) by electrodeposition, and a device for doing so. The device uses an inexpensive, recyclable, pH-neutral electrolyte composed of a glycol compound, a metal chloride, and optionally ammonium chloride. By only applying a small electrical potential, at room temperature, the device can leach a range of valuable metals, such as copper, cadmium or palladium, from a slurry prepared from waste PCBs. Reusing the electrolyte does not degrade device performance and may even increase the amount of metal recovered per electrodeposition cycle. The metal recovery rate is typically from 25% to 70%. In addition to the electrolyte, the device includes a metal or carbon cathode, and an anode that may be a porous carbon material, a metal foam or a conductive polymer foam.
Advantages
- The device is precious-metal-free due to the pH-neutral, chemically benign electrolyte, making it more economical
- The method can be modified to recover a range of valuable metals in e-waste
- Avoids unwanted precipitation of metal ions in the solution
- Unlike other solvents, the glycol electrolyte is recyclable
Applications
- Recycling industries can use the method and device to recover valuable metals from waste printed circuit boards
- Electronics industries can benefit from an inexpensive source of recycled metals needed in mobile devices