New research sheds light on the potential for building more durable infrastructure
Chan Pui-fun
Joint research between City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has identified why adhesives holding certain materials together fracture and fail and what might be done to strengthen these bonds. The research has enormous implications for a wide range of bonded materials, including concrete composites used in Hong Kong’s infrastructure and materials in medical treatments.
According to the research, whenever materials are bonded, such as brick with epoxy or concrete with fibre, the strength and durability of the bonding depends on external factors such as temperature, pH levels and moisture. To improve the bond, it is essential to observe how materials disconnect when they come apart.The findings of the team, which was led by Dr Denvid Lau Tak-bun, Assistant Professor in the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering at CityU, were recently published in a paper, “A robust nanoscale experimental quantification of fracture energy in a bilayer material system”, in the prestigious US science journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
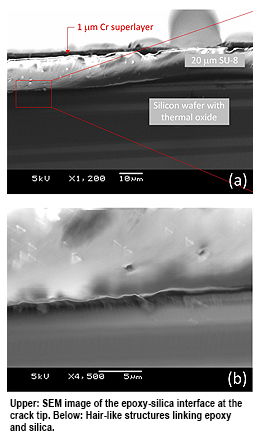
The research measured the debonding mechanism of organic-inorganic interfaces using scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of a layered epoxy (organic)-silica (inorganic) bonded system at the nano level. After debonding, hair-like crack structures were detected that allowed water molecules to seep in and eventually weaken the adhesion.
The new findings will enable engineering researchers to design more durable and reliable composites, which can be applied in all kinds of bonding mechanisms consisting of organic-inorganic materials.A civil engineering scientist, Dr Lau initiated the research on bonding mechanisms in the hope of addressing durability issues such as the effect of moisture on concrete composites, which are used in the construction and structural maintenance of transportation systems, buildings and infrastructure.
“Deterioration or even the collapse of a building will arise if the interfaces between materials are not addressed carefully,” Dr Lau said.
One solution for strengthening concrete is carbon fibre, which has been gaining popularity in the US, Europe and Japan over the past ten years for strengthening worn-out concrete composites. However, carbon fibre is yet to be widely adopted in Hong Kong because of the humid environment. A possible remedy would be to use better sealants for keeping out moisture.
Dr Lau believes the paper was accepted by the influential PNAS journal because of the extensive potential applications of the research beyond the construction industry. Electronic chips, aircraft construction and biomedical treatments, particularly in the field of dentistry, are just a few areas that might benefit from the findings.
“The research findings allow a close and accurate observation of the bonding behaviour of any biomaterials attached to the human body. It will eventually lead to a longer life span of the biomedical applications,” said Dr Lau. Examples include tooth crowns, artificial teeth and silicone gel-filled breast implants.
Collaborating researchers on the paper included Professor Oral Büyük?ztürk and Professor Markus J. Buehler from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Research Associate Mr Kurt Broderick in the Microsystems Technology Laboratories, all of MIT.