Elastic properties of nano diamond revealed for the first time
Catherine Law
In a world’s first, an international research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has discovered that diamonds at nanoscale can undergo ultralarge, fully reversible elastic deformation, findings that could have a profound impact on the nanotechnology and biomedical fields, and even quantum information technologies.
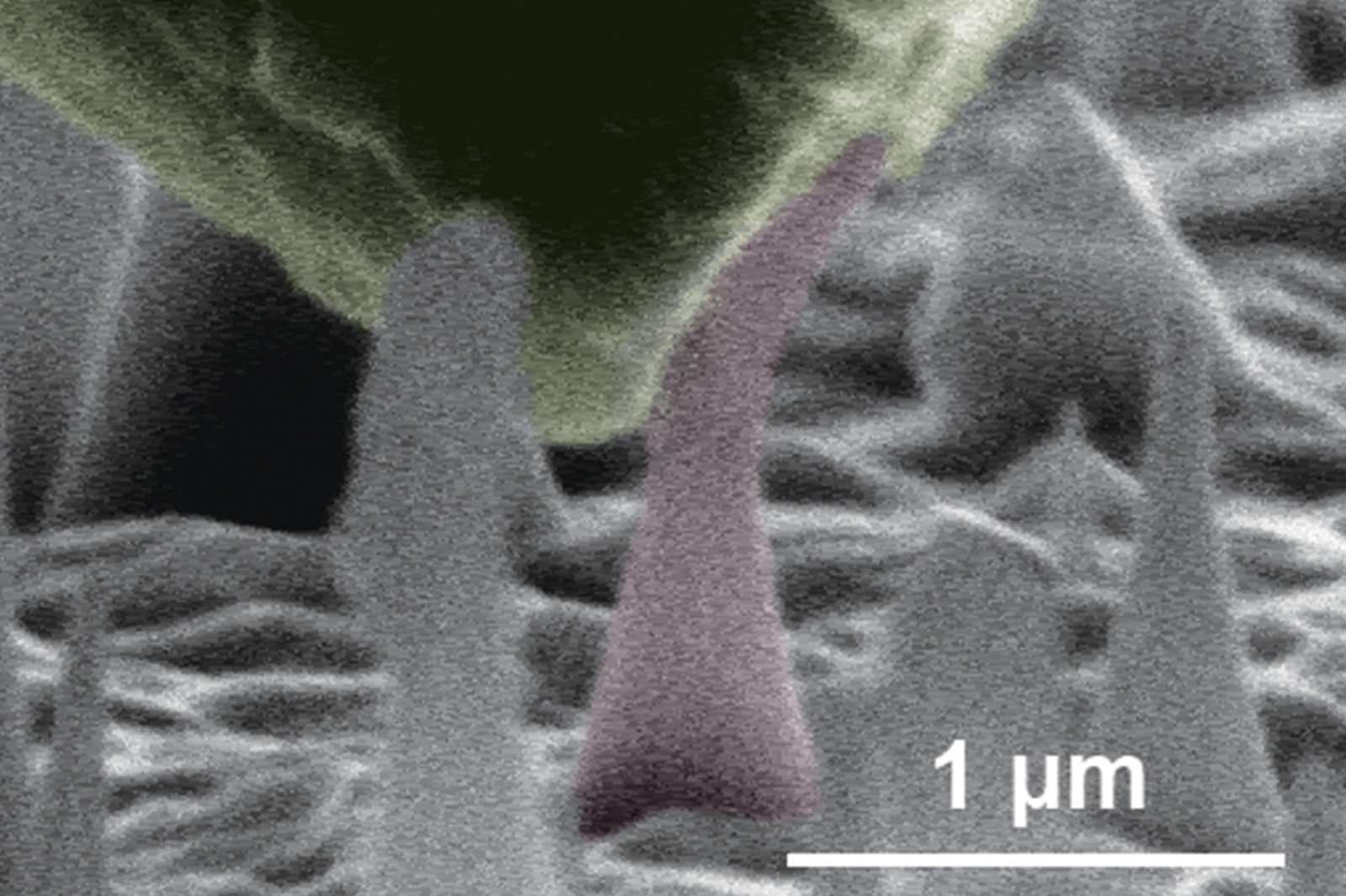
Led by Dr Lu Yang, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering (MBE) at CityU, the research team demonstrated that when diamond was downsized to nearly 100 nanometres in diameter, which is about one six-hundredth of the size of human hair, up to around 9% of tensile elastic strain was recorded for single crystalline samples. The figure is very close to the maximum theoretically achievable strain for an ideal diamond crystal. In contrast, bulk diamond is usually regarded as “undeformable”, with only 0.1 to 0.35% strain recorded in the past.
This groundbreaking discovery was published in the prestigious journal Science this month under the title “Ultralarge elastic deformation of nanoscale diamond”. It was jointly presented by Amit Banerjee and Zhang Hongti, two of the co-first authors of the paper supervised by Dr Lu. The research team comprises materials scientists and mechanical engineers from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, and Nanyang Technological University.
In this project, Dr Lu and his team aimed to characterise the mechanical properties of nanoscale diamonds by using their unique in situ nanoindenter platform inside electron microscopes. The diamond samples were fabricated by Professor Zhang Wenjun of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
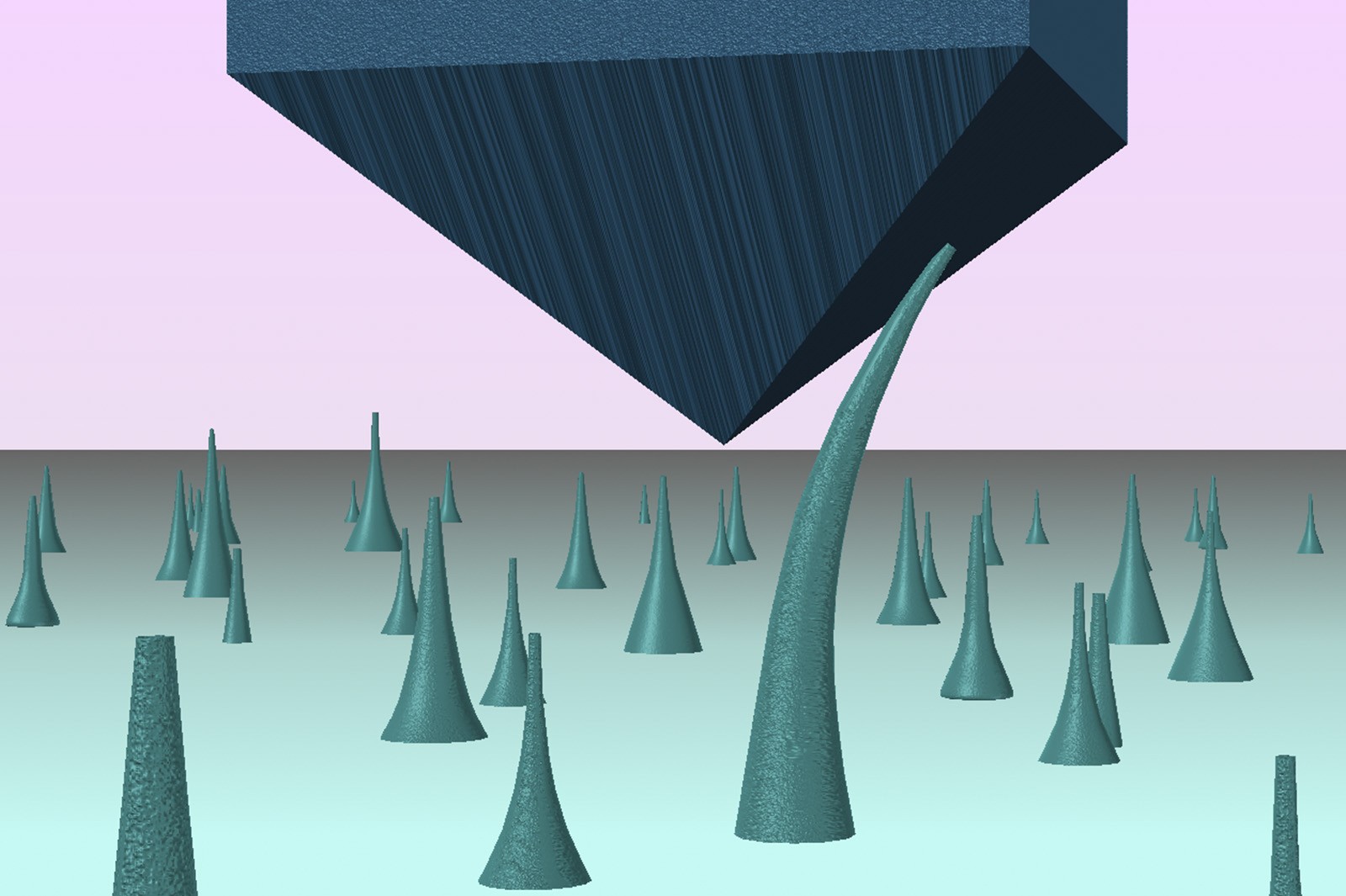
Diamond, the hardest natural material, is often used for cutting and drilling tools as well as to test other materials’ mechanical properties. To tackle the predicament of “diamond against diamond” for this unusual experiment, Dr Lu developed the novel “push to bend” test to exert force onto the diamond nanoneedle from the slant surface of a nanoindenter tip.
The large deformation observed is fully reversible in nature, which implies that the diamond material retains the ability to instantaneously revert back to its original shape when the force causing the deformation is withdrawn, meaning diamond can be elastic.
After numerous overnight experiments, when this surprising result was first discovered in his lab, Dr Lu described the team’s feelings as “extremely exciting”.
“This finding would fundamentally change our common understanding of diamond,” Dr Lu said.
The research holds great promise because diamond is compatible with the human body. One area of possible future exploration is diamond needle-based drug delivery to human cells. “Our discovery on nano diamond’s elasticity can help to make such intracellular delivery to be more durable, and cost-effective, noting that diamond needles are not as brittle as what we perceived,” Dr Lu explained.
“The next generation of information technology could also be based on diamond. Nanoscale diamonds with well controlled point defects can be used for quantum computing and quantum information processing,” said Dr Lu. “Our discovery concerning diamond’s nano-sized characteristics allows manufacturers to produce highly reliable and efficient diamond resonators and sensors for faster data storage and transfer. Future computers will be smaller, lighter and faster,” Dr Lu predicted.
This novel finding may pave the way for diamond’s practical applications in nanomechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, photonics, optoelectronics, and ultra-strength materials.
The research was funded by the Research Grants Council and National Natural Science Foundation of China.