Novel solar cells promise new opportunities
Pioneering research led by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has led to the development of the most efficient all-inorganic inverted perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) to date.
This novel approach will contribute to addressing the global energy issue in a cost-effective manner.
PVSCs are a type of solar cells produced by metal halide perovskite materials, which are an attractive option for the renewable energy technologies due to their high efficiency and low manufacturing cost.
The all-inorganic inverted PVSCs developed in the year-long research project have achieved a recorded efficiency of 16.1% and a certified efficiency of 15.6%. This level of efficiency has great potential to enhance the stability and practical value of PVSCs.
The findings were published in Nature Communications under the title “Highly efficient all-inorganic perovskite solar cells with suppressed non-radiative recombination by a Lewis base”.
PVSCs, especially the organic-inorganic hybrids, have shown remarkable progress since they first emerged a decade ago, with efficiency improving from 3.8% in 2009 to 25.2% in 2019. However, the hybrids are intrinsically unstable at high temperature, and more likely to be influenced by humidity.
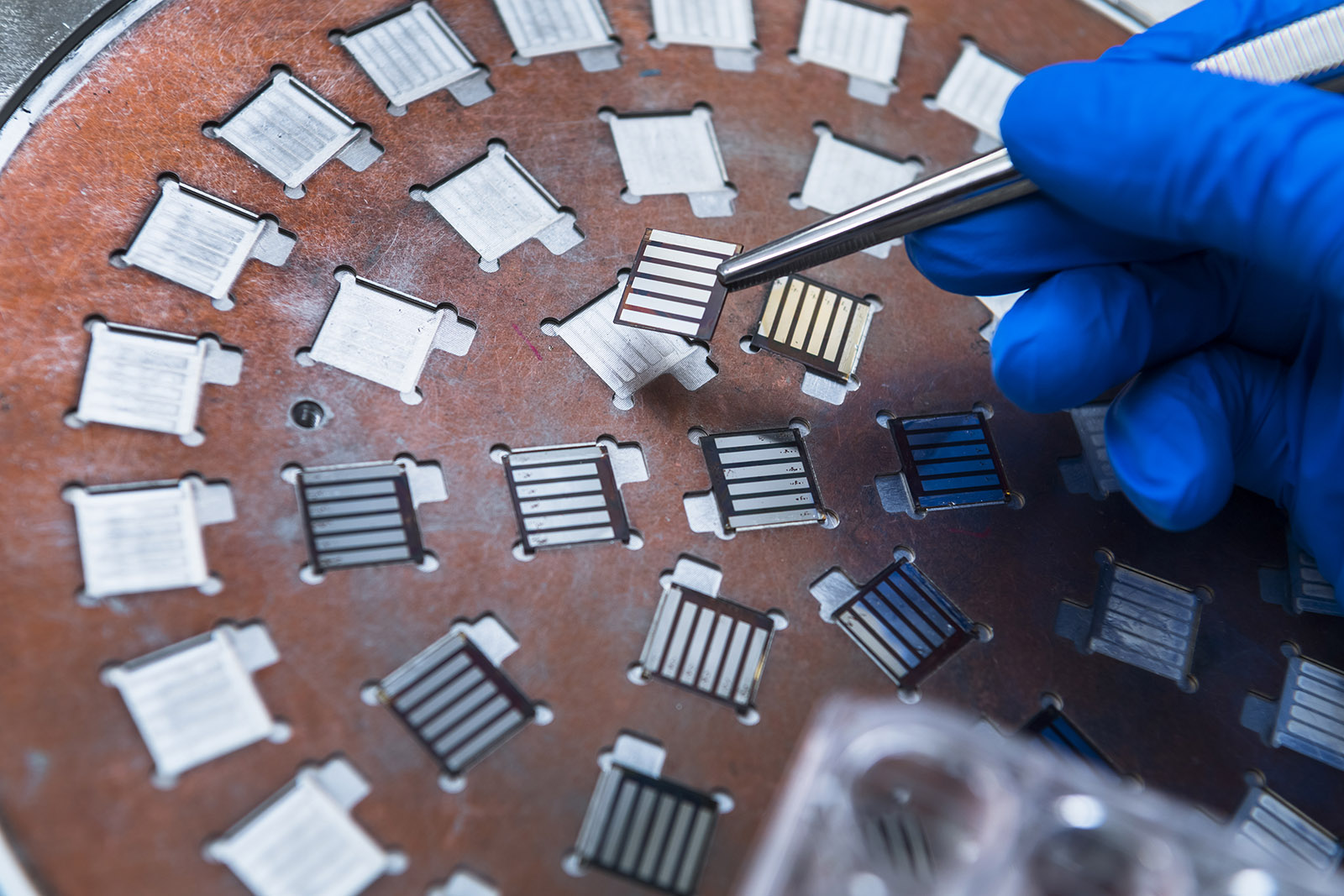
The research team has resorted to all-inorganic PVSCs that demonstrate better thermal and photo stability but which are less efficient. A novel strategy for improving efficiency has been devised, too. It involves a strategy called passivation, i.e. adding an organic functional material during the film fabrication process to eliminate surface defects on the inorganic perovskite film, resulting in the improved efficiency of the PVSCs and enhanced stability.
“Our research has shown that the all-inorganic inverted PVSCs can achieve a 16.1% efficiency, but we can see there’s potential to go higher,” said Professor Alex Jen Kwan-yue, Provost of CityU and Chair Professor of Chemistry and Materials Science.
The future potential of PVSCs will allow roll-to-roll processing with high efficiency, which comes with the added advantage of being semi-transparent. This means future PVSCs could be used as an alternative for building integrated photovoltaics.
“The manufacturing of PVSCs would be like printing newspapers,” said Professor Jen referring to the future of the new technology.
The all-inorganic PVSCs can be very competitive for their high efficiency and thermal stability. “The hope is to provide a similar level of efficiency compared to the organic-inorganic hybrid system,” said Dr Zhu Zonglong, Assistant Professor in CityU’s Department of Chemistry and a member of the research team.
In addition, the configuration of the all-inorganic inverted PVSCs is arranged in a way that’s suitable for fabricating tandem cells. Because an array of tandem cells reacts to different aspects of the sunlight spectrum, the PVSCs in the study have the potential to raise the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the application.
“If only one material is used on the solar modules, only a limited spectrum of sunlight is absorbed, and hence converted to power,” explained Professor Jen. By optimising the materials and interfaces of the solar cell to absorb a wider spectrum of sunlight, the future PCE of the PVSCs using tandem cells is estimated to be over 30%.
Professor Jen, Dr Zhu and Professor Yip Hin-lap from South China University of Technology are the corresponding authors of the paper. The first authors are Wang Jing, PhD student, and Dr Zhang Jie, a postdoctoral fellow from CityU’s Department of Chemistry. Other co-authors include Dr Xue Qifan and Zhou Yingzhi from South China University of Technology, Professor Li Xiaosong and Dr Liu Hongbin from the University of Washington, as well as Professor Chueh Chu-chen from National Taiwan University.