What is Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)?
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a large and diverse class of RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules which has become a growing focus of cancer genomics studies in recent years. In this article, we will explain what lncRNA is and its functions. It is known that the expression level (cellular abundance) of some lncRNAs is associated with disease onset or development, but the mechanism remains unknown. Scientists are trying to explore the mechanism in the hope of developing medical treatments.
What is lncRNA?
The central dogma of molecular biology is “DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) makes RNA, RNA makes proteins, and proteins make us”. The process by which DNA is “copied” to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used as a template to make proteins is called translation.
The human genome contains over 3 billion base pairs of DNA, of which 70% is transcribable into RNA. However, only less than 2% of these RNAs can be used as a template to translate into proteins, which are called “coding RNA”. The vast majority are “non-coding RNA” (ncRNA).
There are different classes of ncRNA, participating in different cellular processes. The one with a length of over 200 nucleotides (the building block of DNA and RNA) is called long non-coding RNA (lncRNA).
What are the functions of lncRNA?
Many studies have found that lncRNA participates in a variety of biological processes, for example, to assemble protein complex, or to regulate coding RNA translation, etc.
Scientists have been actively researching on the functions of lncRNA and so far have revealed many. We can divide these functions into two major categories: 1) assemble proteins; 2) compete for binding with other non-coding RNAs.
1. Assemble proteins
Different lncRNAs have been found associated with many different proteins. The interaction through lncRNAs’ bindings with proteins will determine the lncRNA functions. For example, lncRNA facilitates the binding of transcription factors, a type of protein, to the genome and regulates the expression level of the targeted gene. The transcription factor binding is like a switch to control how much genetic information is “copied” to RNA. See panel C of the below figure.
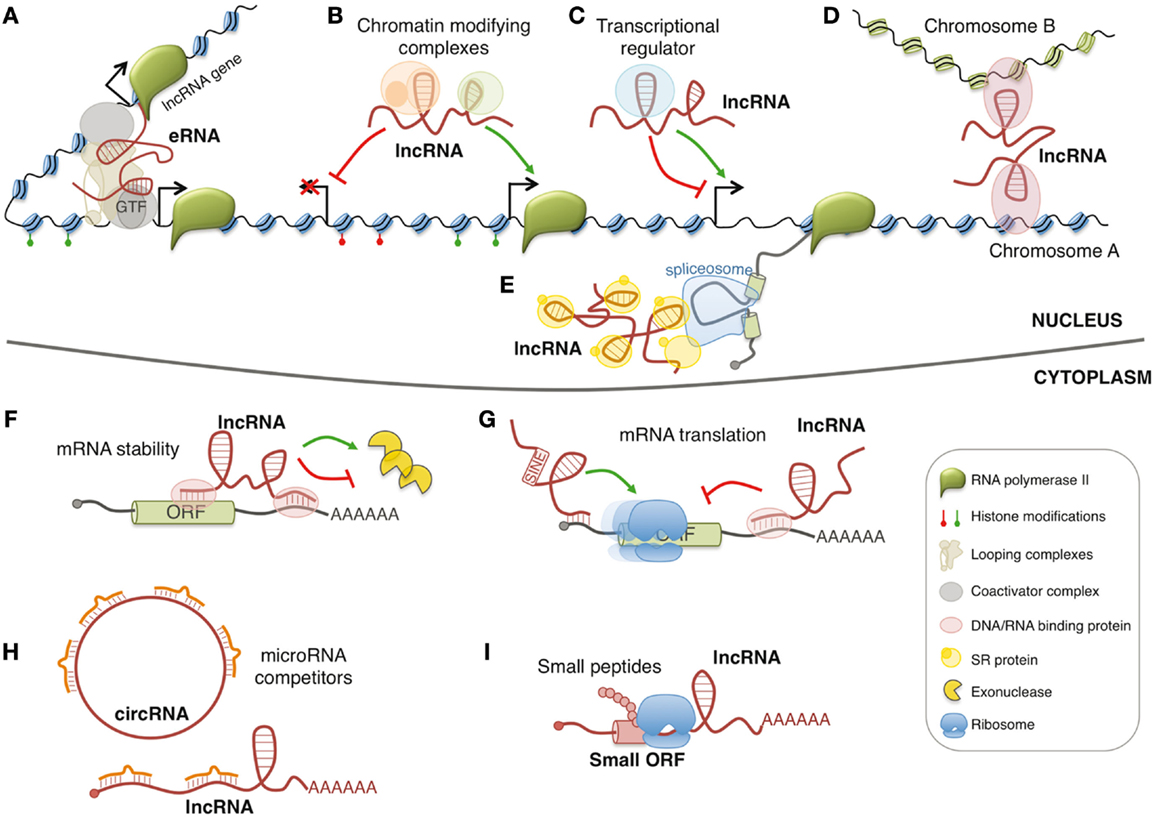
To help understand the functions of lncRNA, a research led by City University of Hong Kong scientists has developed a novel detection method to identify binding proteins of lncRNAs in the living cells.
2. Compete for binding with other non-coding RNA
We know that lncRNA can also compete with messenger RNAs (mRNAs, the molecule that will end up making one specific protein) or circular RNA (circRNA) for binding with microRNA (miRNA, a small non-coding RNA molecule containing about 22 nucleotides). When microRNA binds to lncRNA instead of binding to mRNA, the abundance of mRNA gets increased, and the expression level of genes is regulated. See panel H of the above figure.
In addition to the above two examples, there are also other functions of lncRNA (see the other panels in the above figure). Scientists are still working very hard to explore.
How is lncRNA related to different kinds of diseases?
In some diseases, particularly certain types of cancers, some specific lncRNA expression will get increased. For example:
1) in some of the liver cancer patients, hepatocyte cellular abundance of lncRNA DANCR (Differentiation antagonizing non-protein coding RNA) is significantly higher than the people without liver cancer;
2) in lung cancer, the expression level of lncRNA MALAT1 (metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1) is associated with its prognosis. Sometimes, the level of MALAT1 can be considered as a biomarker for lung cancer metastasis.
However, the detailed molecular mechanisms remain elusive.
What is the relationship between IncRNA & microRNA (miRNA)?
From panel H of the figure above, we can see that lncRNA sometimes competes with mRNA or circRNA for binding to regulatory miRNA and therefore reduces miRNA's availability to its real target (i.e. mRNA or circRNA). So lncRNA sometimes can be considered as “traps” for miRNA, as a natural process used by cells to regulate the abundance of miRNA.
Reference:
- Djebali, S., Davis, C., Merkel, A. et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489, 101–108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11233
- Dunham, I., Kundaje, A., Aldred, S. et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489, 57–74 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11247
- Mongelli Alessia, Martelli Fabio, Farsetti Antonella, Gaetano Carlo. The Dark That Matters: Long Non-coding RNAs as Master Regulators of Cellular Metabolism in Non-communicable Diseases. Frontiers in Physiology 10, 369 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00369
- Igor Ulitsky, David P. Bartel. lincRNAs: Genomics, Evolution, and Mechanisms. Cell 154, Issue 1, 24-46 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.020